LEGO Designer:
Dan Fallon (phreaddee)
Designed:
March 2022
Categories:
All, Earth Orbit Telescopes, Probes and Satellites, Space Agency - NASA
Launch Vehicle Details
Stages:
Length:
Diameter:
Mass at Launch:
Low Earth Orbit Capacity:
Total Thrust:
Apogee:
Class:
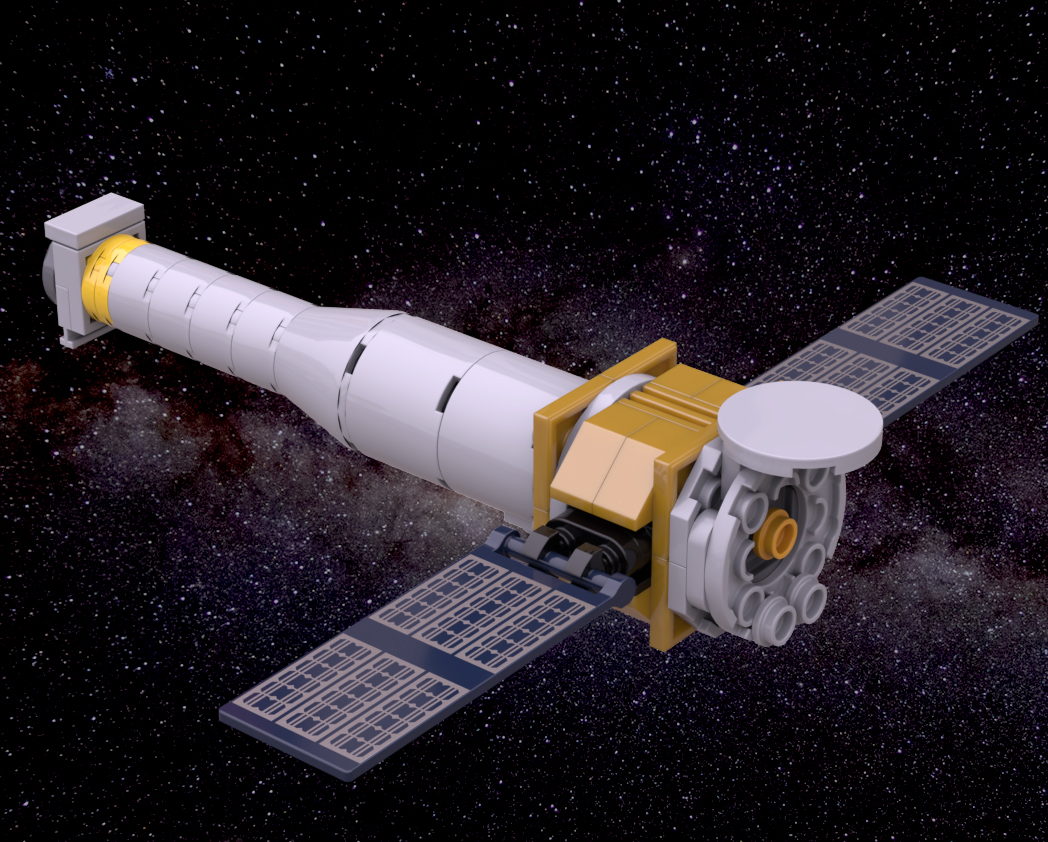
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 100 times fainter than any previous X-ray telescope, enabled by the high angular resolution of its mirrors. Since the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs the vast majority of X-rays, they are not detectable from Earth-based telescopes; therefore space-based telescopes are required to make these observations. Chandra is an Earth satellite in a 64-hour orbit, and its mission is ongoing as of 2022.
Chandra is one of the Great Observatories, along with the Hubble Space Telescope, Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (1991–2000), and the Spitzer Space Telescope (2003–2020). The telescope is named after the Nobel Prize-winning Indian-American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. Its mission is similar to that of ESA’s XMM-Newton spacecraft, also launched in 1999 but the two telescopes have different design foci; Chandra has much higher angular resolution.
Part count: 74 bricks, 31 lots.
| Unit | width | length | height |
|---|---|---|---|
| Studs | 20.5 | 21.7 | 4.6 |
| Inches | 6.5 | 6.8 | 1.4 |
| Centimetres | 16.4 | 17.4 | 3.7 |
No external URL provided.
Launch History information from space.skyrocket.de
Launch History information from space.skyrocket.de
Related Posts
None found

